
The second, a proprietary dewaxing catalyst, selectively cracks straight-chain paraffins.
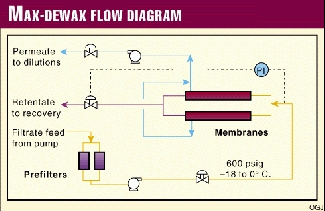
The first is a high-activity desulfurization andĭentrification catalyst, which gives an optimum balance between process objectives and cost. Pretreatment of the feed may not be necessary if the feed is relatively free of organic sulfur and nitrogen. Which improves the hydrocracking performance. Pretreating protects theĭewaxing catalyst and provides a feed with a low organic sulfur and nitrogen content, Olefin saturation, desulfurization, and denitrification reactions. The first stage of the process involves hydrotreatment of the incoming feedstock through Selectively hydrocrack the long-chain paraffinic components in the feedstock. The Catalytic Dewaxing process uses a dual-function, non-noble-metal zeolite catalyst to This entry was posted in Week 05 by Graham Deever. Catalytic dewaxing also allows for the production of light distillates such as gasoline since the n-paraffins are cracking. It is obviously the best way to dewax the feedstocks because it results in a product with lower pour points, high yield, and high stability. There is not much detail to this process although it does use hydrogen addition to prevent coking.

It uses catalytic cracking of n-paraffins, but since the purpose is to remove wax, it is classified as a separation process.

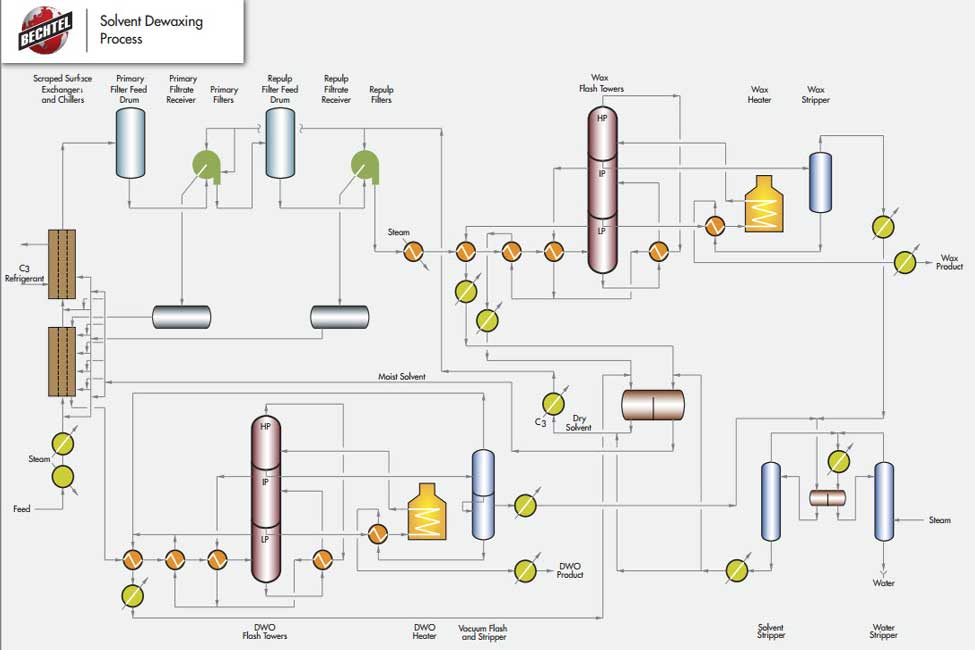
Most refineries use MEK even though propane can be used from multiple aspects of the process, save money, increase filtration rates.Ĭatalytic dewaxing is a chemical process that, by nature, is actually a conversion process. Issues that arise from this process come from choosing which type of solvents to use. The wax goes on to produce candle wax and petroleum jelly while the dewaxed oil purifies into the desirable lube oil base stock. The MEK solvent and the deasphalted oil combine in the first phase and go through a series of refrigeration processes at different temperatures to form wax crystals, which are then transported to a rotary filter where a filter cloth separates the wax from the oil + solvent. Solvent dewaxing is a physical process that uses refrigeration, scraping techniques, and methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) and propane solvents to separate the feedstocks and produce a valuable product. There is two different processes that result in this marketable lube oil: solvent dewaxing and catalytic dewaxing. The goal of dewaxing is to remove hydrocarbons that would potentially increase the pour point of the lube oil base stock to a desirable range of -9 o – 14 o F. Dewaxing is a separation process that takes advantage of deasphalted oil (DAO) and heavy vacuum gas oil (HVGO) from the vacuum distillation tower as feedstocks in producing lubricating oil base stock and, to some extent, distillate fuels such as gasoline.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
